Introduction #
Like every other program running on your VPS or Dedicated Server, Apache is a piece of software that serves the purpose of a Web Server. The job of a typical Web Server is to serve web requests made to websites hosted on the Web Hosting Server.
For example, if one of your visitors requests your domain, “domain.com”, from a web browser, Apache will then serve the index page for domain.com as a response to the request. Knowing about the current status of Apache is useful when you are facing issues with your website’s pages not being served or when you are experiencing slow loading speed for those. The “Apache Status” feature in the WHM control panel will give you all the information you need to troubleshoot such issues and in the next lines of this tutorial, we will show you how easy it is to use it. Let’s get started!
Accessing the Apache Status feature #
First, you need to log into the WHM service for your VPS or Dedicated Server. After you have logged in, please use the search bar on the left side of the page and type “Apache Status”.

When the functionality shows up below the search bar, please click on it so you can be sent to the “Apache Status” page.
Reading information from the Apache Status page #
When you first land on this page, you will notice the first section which will contain really basic information about Apache. More specifically its version, its current MPM module, and the date and time when Apache was installed on the server.
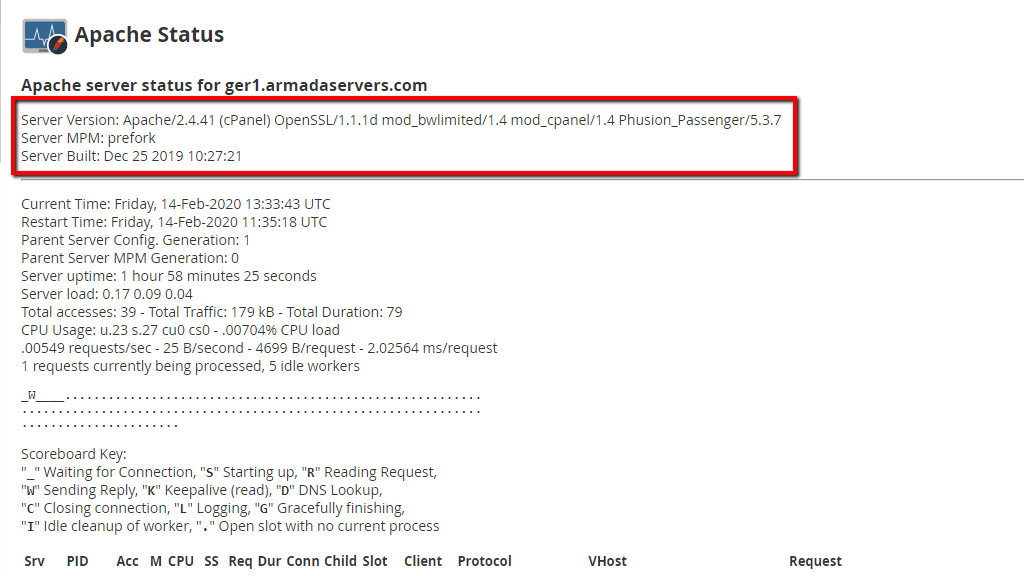
The second display will contain the following information.
- Current Time – Shows current time and date.
- Restart Time – Shows the time and date of the last Apache restart.
- Parent Server Config Generation – This shows the number of times that Apache has been gracefully restarted, which causes it to re-read its configuration file. This may occur, for example, whenever a domain is added to your server. What happens then is that a new vHost entry is added in the configuration file and for it to take effect, Apache must be restarted.
- Server uptime – This displays the uptime of the Apache service.
- Server load – This displays the current server load.
- Total Accesses – This shows you the total number of requests on your server.

The next section is “Scoreboard Key”. It shows information about the Apache workers and their current mode. The section below will represent all of the available slots Apache has for requests.
- _ – This shows that this worker is currently waiting for connections.
- S – This shows that the worker is starting to process a request.
- R – This shows that the worker is reading the request.
- W – This shows that the worker is currently sending a reply.
- K – This means that the worker is in staus “Keepalive” and is reading the requests.
- D – This means that the worker is currently performing a DNS lookup.
- C – This means that the worker has finished its job and is closing the connection.
- L – When the worker is in this mode it is logging information.
- G – This will show that the request is being gracefully finished.
- . – This will display an open sloth with no current process.

Bellow the scoreboard you will see a table section, displaying the current requests Apache is processing. Let’s go over the columns and explain them.
- Srv – This will show the worker’s server number.
- PID – This will display the system ID of the operating system’s process.
- M – Shows the current work’s mode.
- CPU – This shows the worker’s current CPU usage.
- SS – This will display the number of seconds since the start of the most recent request.
- Req – This will show the time it took for the worker to process the most recent request.
- Child – This will be the total amount of information the worker transferred.
- VHost – This will show the domain name that requested the data.
- Request – This will be the type of request the server received.

There you have it! Please note that in this guide, we have attempted to capture the most relevant parts of this page. Apache is a really complex system and there is a lot of information available on its official documentation page, which we cannot simply cover in a single tutorial. However, if you have any questions about this specific feature or you are unaware of what something means or does, please, feel free to contact our Technical Support Team over the ticketing system in your Client Area.



